1. Introduction
This guide provides technical guidance for the design, use of materials and workmanship for podium decks to meet the functional requirements of the LABC Warranty Technical Manual.
Examples of podium decks include:
- An open amenity space above a sub-terrain car park
- A terrace
2. Definitions
Podium Deck
Podium decks are an open spaced amenity structural slab / deck and are defined for warranty purposes as "an externally weathered elevated platform over an unconditioned (unheated or soundproofed) space."
The requirement to waterproof is to:
- protect the deck surface from water accumulation, and
- prevent the ingress of water to the space below, and
- prevent ingress of water to adjacent buildings.
Where a space below a proposed deck is conditioned (heat and sound), it would no longer be considered as a ‘podium’ and instead is classified as an insulated flat roof deck.
Please refer to BS 6229:2018 – Flat roofs with continuously supported flexible waterproof coverings - Code of practice, and additional Technical Manual guidance for Roofs.
Transfer Deck
A transfer deck is a uniquely loaded supporting podium deck. The designed vertical superstructure loads supported from the deck are transferred along a horizontal load path along designed beams integral with the slab to new supports.
The requirement to waterproof is to:
- protect the deck surface from water accumulation and
- prevent the ingress of water to the space below and
- Prevent water ingress into buildings supported on and adjacent to the deck.
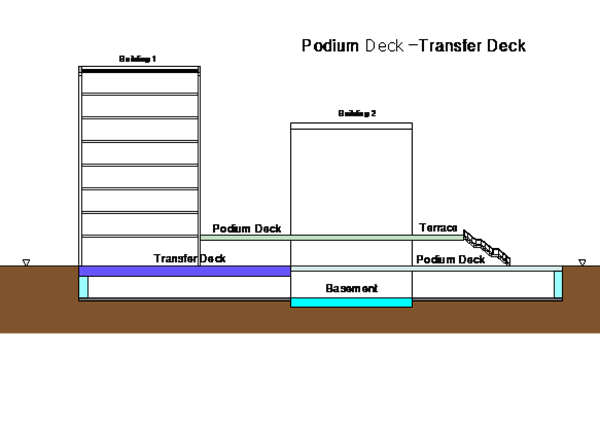
Typical podium deck and Transfer deck examples
3. Design considerations
Design intent
For the elemental design of a Podium Deck, the client must provide a clear indication of the surface usage and its possible future use.
The design should demonstrate a satisfactory level of:
- Structural performance of the slab for surface treatment, finishes and drainage
- Architectural and landscaping placed on the podium deck
- Management of surface water around landscaped features to drainage points.
- Drainage from the podium deck
Technical Standards
In the design of a podium deck, reference to other associated technical standards may be appropriate. Examples include:
- Continuous Membrane Roofing
- Green Roofs
- Blue Roofs
- Drainage
- Basements
Waterproofing Design
If the space beneath the podium deck is below ground, the design of the waterproofing layer must be coordinated alongside a CSSW qualified structural waterproofing specialist.
Associated Design Principles
- The principles of BS 6229: 2018 Flat roofs with continuously supported flexible waterproof coverings – Code of Practice: are to be applied to waterproofing of podium decks to ensure water ingress does not occur.
- BS 8102:2009 – Code of practice for protection of below ground structures against water from the ground: are to be applied to ensure the continuity of waterproofing of junctions of basements to podium decks is managed to ensure that water ingress does not occur.
Further practical guidance on this and compliance with Warranty requirements for podium decks is included herein.
Guidance limitations
This guidance is not intended as a standalone design guide and does not include full details of what must be considered to comply with other associated design guides. See Section 6 - References and Further Guidance.
4. Design requirements
Information required
To allow a Warranty assessment to be undertaken in a timely manner, developers must provide information at the earliest opportunity. At submission a full design should include:
Drawings
- General Arrangement Plans for each podium deck area showing
- Deck features and landscaping
- Directions of falls for surface water management
- Drainage provisions
- Deck finishes
- Below slab space
- General Sections and Section Details for
- Layering / build up types above the slab showing waterproofing, water flow control and finishes
- Variance of build-up types
- Movement joints
- Entrance thresholds
- Building abutments and upstands on and adjacent to podium deck
- Through slab services and pipe penetrations
- Planters and Green landscaping
- Slab fixings
- Other base details for architectural features placed on the slab
Design and Materials
- Slab design and deflection analysis
- Surface water drainage design philosophy and peak flow calculations for entire podium slab (including countersunk outlets)
- Specification of component materials and products used, including third party accreditation certification.
- Maintenance plan to address how remedial works could be undertaken in the event of a defect.
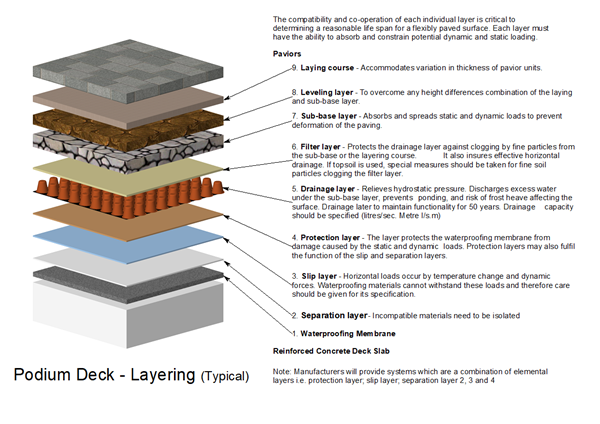
Podium Deck Use
At the earliest possible pre-construction stage, the client design should define the range of potential uses of the podium deck with reference to the worst case of dead loads (permanent finishes), live imposed (use types) and rolling (traffic) loads. Detailing should be undertaken to ensure that in the event of a defect, a repair can be feasibly undertaken and should be at the forefront of the design process.
Landscaped areas requiring water irrigation will require additional control of surface water. Please refer to the Warranty Green Roofs guidance for further information.
Surface water attenuation systems – Blue roofs on the Podium Deck will require additional structural analysis of the deck and drainage control. Please refer to the Warranty Blue Roofs guidance for further information.
Substrate – The Podium Deck Slab
Podium Decks constructed from reinforced concrete and correctly designed by a competent engineer have proven to be the most reliable when designed in accordance with BS EN 1992-1-1:2004 Eurocode2 Design of Concrete Structures (+A1:2014). In any event the substrate in all cases must be proven to be dimensionally stable.
For Warranty purposes, Podium Decks constructed of block and beam floors or pre-cast concrete planks are not acceptable for any podium deck applications.
Other approaches such as pre-cast concrete hollow core planks with a structural screed and ribbed metal deck formwork require additional specialist involvement to demonstrate that the construction will meet the requirement to show that the substrate will be dimensionally stable.
When there is any risk for excessive movement as a result of the substrate selection or any potential future use of the deck area increasing slab movement, the designer must ensure through clear evaluation and demonstration that the system is able to cope with the worst case anticipated movement.
Deck falls
Drainage falls should be constructed in a manner that they fall away from any structures built off the podium. Water standing on the deck, can exert pressures laterally on the external walls of structures built over the deck, therefore, the waterproofing line from the podium deck surface must be continuous to DPC level.
Cementitious screeds provide a stable substrate to mitred falls and are recommended. Screeds to be in accordance with BS 8204. Surface water should always fall away from any above deck protrusions or abutments.
The finish surface is to have a minimum design fall 1:80 prior to applying the waterproofing layer. This will ensure that adequate flow of surface water is maintained to the drainage system and that no ponding occurs on the deck.
Consideration should be given to height differences between the top and bottom of the falls. Where there are large height differences in the screed forming the falls the height for dressing the waterproof membrane up an abutment wall may be reduced.
On large podium decks it may be necessary to increase the number of drainage outlets to avoid excessive fall heights in the screed.
Waterproofing
Fully bonded or monolithic systems are typically appropriate for Podium Deck waterproofing. Any waterproofing system must not allow the ‘tracking’ of water under the waterproof membrane.
Curing agents may, on occasion, be applied to the top surface of the concrete substrate to:
- Enhance the concrete quality and durability
- Reduce the curing period
The curing agent essentially forms a membrane across the concrete surface of the laid concrete to increase the density of the cement paste and lower the porosity at the surface. This increases resistance to external influences, surface stresses and attack.
Applied curing compounds are not always compatible with a proposed hot-melt application adhesion may be reduced causing delamination from the substrate and potentially cause water to track under the waterproof layer following a membrane failure.
Compounds based on a sodium silicate based are generally acceptable for a direct applied hot-melt waterproofing application. Adhesion reduction is likely when the base component of the curing agent is:
- Acrylic and chlorinated rubber
- Resin
- Wax
- Wax/Resin
In all cases, hot-melt waterproofing membranes must be applied to a primed concrete surface with reference to BS EN 13670:2009 Execution of Concrete Structures (E) - 8.5 Curing and protection states (10) (11).
All ‘systems’, specified products and materials require a 3rd party product approval certification such as BBA or other harmonised European Standard which references the areas the material can be used. In the selection of a system, it should be considered whether that system is reliant on insulation or a ‘Water flow reducing layer’ to disperse water to the outlets.
For Podium Deck applications, loose laid or partially bonded waterproofing materials are not acceptable.
The use of a ‘waterproof concrete’ is not considered to be an acceptable approach for Podium Deck waterproofing.
As soon as is practically possible, the waterproof membrane will require protection against damage from either follow on trades or the deck being used as material storage space.
Prior to applying surface finishes above the waterproof layer, the waterproof membrane must be integrity tested and verified by an independent third party. See Section 5 - Testing.
The waterproofing layer must be linked to any cavity tray to avoid discontinuity which could result in moisture ingress.
Drainage
A complete drainage design for the Podium Deck must be provided, by a suitably qualified and experienced engineer and in accordance with BS EN 12056-3:2000. Drainage calculations should be accompanied with a short explanatory statement including assumptions made.
It is important that the Podium Deck be designed to adequately deal with the predicted rainwater for its geographical location. Additional consideration should be made for drainage from upper areas such as façade run off or external balconies from the adjacent structure(s).
Surface water from upper podium levels or roofs must not discharge onto lower podium deck levels.
Podium deck surface finishes shall be positively drained to discharge surface water so that it does not accumulate and it does not compromise the use of the space at surface level.
Where a green / Blue roof proposal forms part of a podium deck proposal, our Warranty guidance on Green and Blue roofs must be followed as such proposals may impact on the Podium deck performance. (Loadings and effective drainage)
Rainwater outlets
- Should be positioned in the locations of maximum deflection.
- Outlets within the slab must be designed to be countersunk and discharge at deck level, not at surface finish level.
- The waterproofing layer must be dressed into the outlets.
- Inlet gullies which collect water from the deck and finishes level and then discharge directly onto the waterproof membrane should be avoided.
Where podium decks form part of an enclosed area, an overflow for each outlet required, should be provided to ensure that surface water does not accumulate in the event of a blockage. Surface water should be discharged through the external perimeter in a readily apparent location to allow for maintenance to be undertaken at the earliest opportunity.
Movement Joints
Structural movement joints are required in large area reinforced concrete Podium Decks. Detailing of all movement joints are required to demonstrate they will prevent water ingress or accumulation of water adjacent at or local to the joint to limit the risk of frost-thaw action.
Materials forming the movement joint must be durable and be able to flex with the waterproofing membrane. Joints must be accessible for inspection and maintenance to allow for repair in the event of a defect.
Abutment Joints
Abutment joints with isolated vertical construction adjacent to the Podium Deck should not permit the ingress of water to the space below.
Allowance should be made in the detailing for anticipated movement between the Podium Deck and the vertical façade, to prevent the waterproof layer from shearing.
Where structures abut or are built off the podium deck, the waterproofing must be dressed up the vertical surface of the facade to a minimum of 150mm above the finished Podium Deck level.
Cavity trays above abutments (Podium Deck to Wall junctions) are often breached at the podium deck level, allowing water to seep into the building. Continuity is therefore essential between these two elements and waterproofing detailing is required to ensure any water passing the cavity tray is discharged to the podium deck adequately. Waterproofing layers must be linked with the DPC which should be at least 150mm above the finished surface level. The masonry should be durable against saturation in accordance with BS EN 771-1.
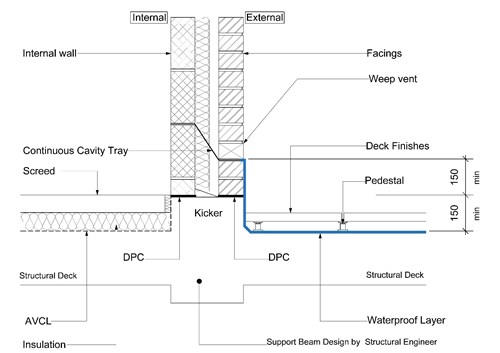
Podium deck – wall waterproofing detail (Slabs on pedestals)
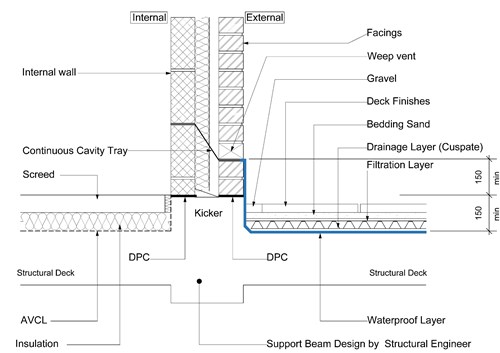
Podium deck – wall waterproofing detail (Bedded slabs)
Threshold abutments
All Level door accesses formed from the podium deck level to occupied spaces should provide
- A 10mm gap between the drainage channel and the door cill &
- The door cill should have a minimum 45mm overhang of the construction below
- In order to have a reduced upstand of 75mm max from the underside of the door cill to the top of the structural deck, there must be a fall on the structural deck away from the door opening.
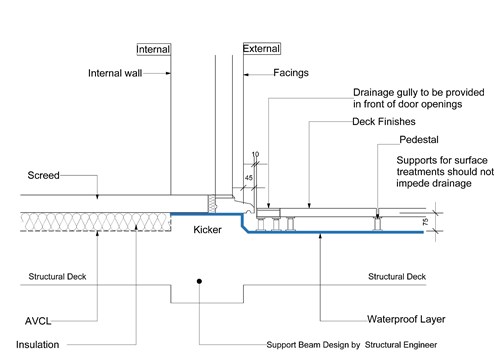
Podium Deck- Threshold waterproofing detail (Slabs on pedestals)
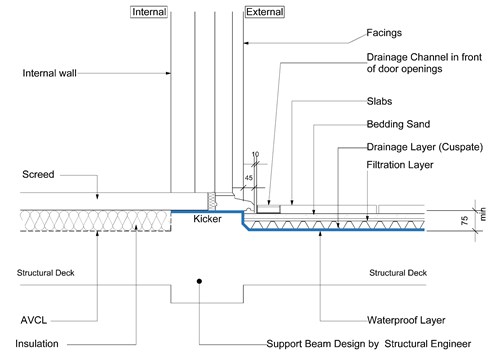
Podium deck – Threshold waterproofing detail (Bedded paviours)
Slab Penetrations
Where possible, it is best to avoid Podium Deck penetrations for service provisions. Where required, the designer should look to group the services to minimise the necessary number of penetrations.
Detailing of the penetration or group to prevent ingress or accumulation of water at the penetration requires consideration and should ensure:
- Back falls are not created at service penetrations.
- Waterproofing must allow for potential movement with the service penetration detailing
- Waterproofing must be fully bonded and compatible with the service pipe material.
- The Waterproofing must extend 150mm above Podium Deck surface finished level.
Architectural features
At the pre-construction phase, an audit of the surface treatments, architectural features and planters that are placed on the podium should be established. Such detailing will require the need for
- Weatherproofing - incorporating an upstand and cover flashing arrangement for solid features placed on the Podium Deck, or
- Waterproofing - providing continuous waterproofing under the architectural feature.
- Diversion – measures should be taken to divert water around large structures to ensure that it is able to reach the outlets provided
Where structures are built off the Podium Deck, a suitably designed 150mm upstand above the waterproofing layer must be provided. Surface water should be designed to fall away from any structures built off the podium.
Planters should be built off a 150mm monolithic kicker with the Podium Deck slab.
5. Installation Requirements
Construction Evidence
A quality assurance and record keeping system should be provided at preconstruction to ensure that standards of workmanship can be demonstrated.
An approved installation contractor recognised by the material manufacture as being competent to install the manufacturer’s waterproof membrane should be used. Evidence of the manufacturer’s approval of the contractor to install their products should be provided to the Warranty surveyor.
The waterproof layer of the podium deck shall achieve a minimum design fall of 1:80 – ‘as built’. A levels survey should be undertaken to demonstrate this is achieved.
Testing
Testing is required to demonstrate the integrity of the waterproof membrane.
It must be undertaken by a suitably qualified and experienced third party certified test agency who is independent of the roofing contractor using either
- Low Voltage Earth Leakage or
- High voltage electrical discharge
Additional testing may be required where by inspection, there is potential that defects may have occurred as a result of damage from follow on trades, or the deck being used as storage.
Certification should be made available to the Warranty surveyor prior to handover. The testing service provider should provide in their report:
- Date of Test
- Project Name, Address and Reference Number
- Name, Address and Contact of certifier
- Description and efficacy of the waterproof installation.
- Experience and training of tester
- Membership of an appropriate trade association, that sets a Code of Conduct for the service
- Details and provision of large- clear photographs of defects identified (when applicable)
- Number of tests undertaken
- Confirmation of result of testing
Final Inspection
At practical completion of the waterproofing to the Podium Deck. All areas should be clear of stored material, site operations and all protection. A thorough, visual and recorded inspection, of all areas, including deck surface architectural and landscaped features, to be carried out with representation from the main and roofing contractors in attendance.
6. References and further guidance
References (September 2021)
- BS EN 1992-1-1:2004+A1:2014 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures. General rules and rules for buildings
- BS 6229:2018 – Flat roofs with continuously supported flexible waterproof coverings - Code of practice
- BS 8102:2009 – Code of practice for protection of below ground structures against water from the ground
- BS EN 12056-3:2000 – Gravity drainage systems inside buildings - Roof drainage, layout and calculation.
- BS 8204-1:2003 Screeds, bases and in situ floorings. Concrete bases and cementitious levelling screeds to receive floorings – Code of Practice (+A1:2009)
- BS EN 13670:2009 Execution of Concrete Structures
Guidance Notes:
- SWG2/12.13 – Property Care Association Podium Decks

